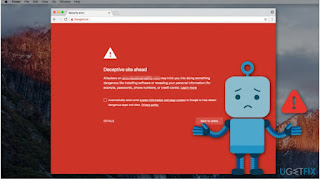
Google says our site is "Unreliable and has harmful claims and must fix". This is an example of big tech censorship that has gone wrong. Google is never specific about what it feels is harmful. It makes broad generalizations about their claims with no specifics.
Google does not allow content that:
- Makes claims that are demonstrably false and could significantly undermine participation or trust in an electoral or democratic process.
- Promotes harmful health claims or relates to a current, major health crisis and contradicts authoritative scientific consensus.
- Contradicts authoritative scientific consensus on climate change.
- Unreliable and harmful claims
Google does not allow content that:
- Makes claims that are demonstrably false and could significantly undermine participation or trust in an electoral or democratic process.
- Examples: information about public voting procedures, political candidate eligibility based on age or birthplace, election results, or census participation that contradicts official government records
- Promotes harmful health claims, or relates to a current, major health crisis and contradicts authoritative scientific consensus.
- Examples: Anti-vaccine advocacy, denial of the existence of medical conditions such as AIDS or Covid-19, gay conversion therapy
- Contradicts authoritative scientific consensus on climate change.
- Misinformation and deceptive practices: Google has guidelines against the dissemination of false or misleading information, scams, or deceptive practices that can harm users or mislead them.
Google has faced pressure from governments to remove or restrict certain content
Google's approach to content moderation and censorship has been a subject of debate and scrutiny over the years. Here are some key points to consider:
- Content moderation policies: Like many other online platforms, Google has content policies in place to regulate the type of content that is allowed on its platforms. These policies are designed to ensure user safety, prevent the spread of harmful or illegal content, and maintain a positive user experience.
- Regional variations: Google's content moderation policies may vary depending on the country or region due to legal requirements, cultural sensitivities, or local regulations. This can result in differences in search results or the availability of certain services in specific locations.
- Government requests and censorship: In some cases, Google has faced pressure from governments to remove or restrict certain content, either due to legal requirements or political reasons. This can lead to instances of censorship, where access to information is limited or blocked.
- Transparency reports: Google publishes regular transparency reports that provide information about government requests for content removal and data disclosure. These reports offer insights into the extent of censorship or content restrictions imposed by governments.
- Algorithmic influence: Google's search algorithms play a significant role in determining the visibility and ranking of search results. Algorithm updates and adjustments aim to improve the relevance and quality of search results, but they can also inadvertently impact the visibility of certain content.
It's important to note that discussions around Google's content moderation and censorship are often complex and multifaceted. Different stakeholders may have varying opinions and concerns regarding the balance between free expression, user safety, and compliance with local laws. It is recommended to stay informed by referring to credible sources and engaging in discussions surrounding internet governance and freedom of speech.
Negative aspects of Google:
- Monopoly concerns: Google's dominant position in the search engine market has led to concerns about its influence over online information and competition in the industry.
- Potential for misinformation: While Google strives to combat misinformation, false or unreliable information can still appear in search results due to the vast amount of content available on the internet.
It's important to approach any online service or platform with a critical mindset and be aware of potential risks and limitations. Users should take precautions to protect their privacy, verify information from multiple sources, and exercise digital literacy skills to navigate the online world effectively. Ultimately, whether Google is harmful or not depends on how it is used, the specific context, and individual perspectives.
Big Tech & Google Censorship Is A Real Problem
During the pandemic, Google implemented various measures to provide reliable information and combat the spread of misinformation. For example:
Information panels and authoritative sources: Google displayed information panels and promoted reliable sources, such as the World Health Organization (WHO) and Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), for COVID-19-related searches. These panels aimed to provide accurate information and counteract misinformation.
Fact-checking and content policies: Google's content policies were enforced to restrict the spread of false or misleading information about COVID-19. They collaborated with fact-checking organizations to review and label misinformation in search results or on platforms like YouTube.
There have been several notable instances of content moderation or censorship by big tech companies. Here are a few examples:
YouTube demonetization and content removal: YouTube, owned by Google, has faced criticism for demonetizing or removing videos and channels that were deemed to violate its content policies. This has affected various content creators, including political commentators, controversial figures, and alternative media channels.
Twitter content removal and suspensions: Twitter has been involved in numerous cases of content removal and account suspensions. For instance, Twitter has suspended accounts for violating its policies on hate speech, harassment, or promoting violence. The platform has also faced criticism for perceived bias in content moderation decisions. Hopefully, this is now corrected that Elon Musk has purchased Twitter and fired numerous executives.
Facebook's fact-checking and content removal: Facebook has implemented fact-checking mechanisms and content removal policies to combat misinformation and false news. While this is intended to curb the spread of unreliable information, there have been concerns about potential biases and the impact on free speech.
Amazon's removal of books and products: Amazon has faced controversy over its removal of books or products from its platform. This includes instances where books were removed due to controversial or objectionable content, or products were delisted based on policy violations.
Does this censorship by Google create the opposite effect and drive more people to actually take an interest in the content and understand the truth? Time will tell . . .